The Purpose of Obstetric Ultrasound and Its Benefits Afterward
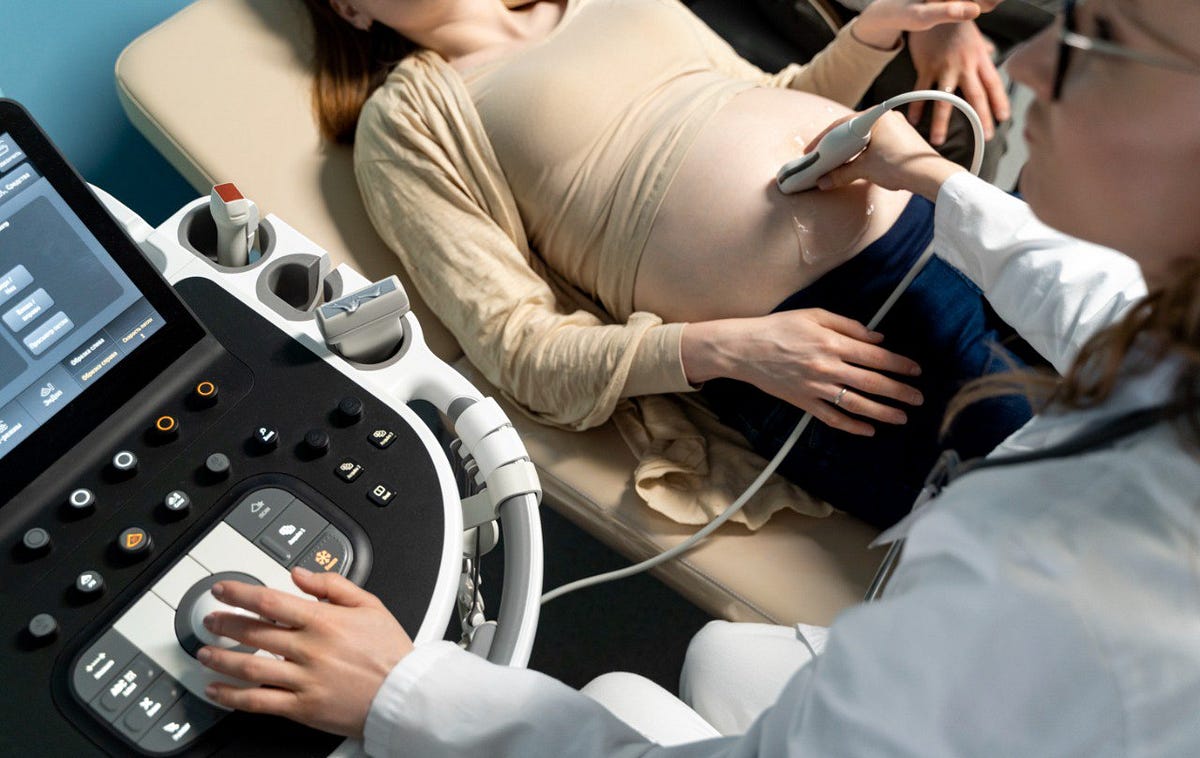
The goal of obstetric ultrasonography is to offer a precise, safe, and non-invasive way to assess the uterus and foetus clinically. The assessment begins as soon as a viable (living) pregnancy is confirmed and continues for the duration of the woman’s pregnancy.
One type of radiological evaluation is ultrasound imaging. Sonography, ultrasonography, or ultrasound scan are other names for it. It is comprised of a transducer, a tiny probe that is applied directly to the skin.
The transducer is placed after a gel has been applied to the skin. Through the gel and into the body, the transducer sends high-frequency sound waves into the body. The tissues absorb sound, which is then reflected back to the transducer. Electrical impulses that are perceived as black and white pictures are created from the sound waves.
Why is obstetrics ultrasound performed?
Every three to four weeks, an obstetric ultrasound is carried out to track the developing foetus and the mother during pregnancy.
First-trimester obstetric ultrasound
First, an ultrasound is done to make sure the pregnancy is viable. Either trans-abdominal (the transducer is positioned over the abdomen) or trans-vaginally (the transducer is narrow and inserted into the vagina) procedures are available. Sometimes, both may be carried out at the same time.
Pregnancy should not be 13–14 weeks along when it is done. Early miscarriage diagnosis and the presence of multifetal gestations (several foetuses, such as twins or triplets) can both be made with the use of a first trimester ultrasound examination. Anatomical anomalies and diseases can be found in the mother’s reproductive system by evaluating it with an ultrasound performed during the first semester.
Ultrasonography in the second and third trimesters aids in evaluating the growth and anatomy of the foetus. Evaluations of the foetal position, amniotic fluid volume surrounding the foetus in the uterus, placenta placement, foetal heart activity, foetal spine, and foetal abnormalities can also be part of an obstetric ultrasound examination.
There may yet be a chance to end the pregnancy if foetal abnormalities are found between weeks 18 and 20. The estimated foetal weight and amniotic fluid can be calculated, the mode of birth can be ascertained, and the fetus’s health can be monitored with the aid of ultrasound monitoring. Usually, foetal growth assessments are carried out every three to four weeks.
if you are preparing ultrasound certification course join StudyUltrasound. StudyUltrasound is the best platform to learn Ultrasound. I hope this information was useful to you. I hope your pregnancy goes well!

Comments
Post a Comment